How is Diabetes Managed?
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by high blood sugar levels due to either the body’s inability to produce insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or the body’s inability to use insulin effectively (Type 2 diabetes). Proper management of diabetes is crucial to prevent complications and maintain a healthy lifestyle. In this article, we will explore the key aspects of how diabetes is managed.
Medical Care and Monitoring:
Diabetes management begins with regular medical care and monitoring. If you are diabetic, you will need to work closely with healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, and dietitians, to develop a management plan, personalized to your specific needs.
Regular check-ups, blood tests, and monitoring of blood sugar levels are essential to assess the effectiveness of the management strategies and make necessary adjustments.
Healthy Eating:
A balanced and healthy diet plays a crucial role in managing diabetes. The primary goal is to regulate blood sugar levels by controlling the intake of carbohydrates. Individuals with diabetes should focus on consuming whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Portion control is vital to prevent spikes in blood sugar levels. Monitoring carbohydrate intake through carbohydrate counting or the glycemic index can be helpful. Consulting a registered dietitian can provide personalized dietary guidance.
Regular Physical Activity is a Must:
Physical activity is essential for managing diabetes. Engaging in regular exercise helps lower blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and maintain a healthy weight.
Aerobic exercises like walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling, along with strength training, are recommended. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting an exercise regimen to determine the appropriate intensity and duration based on individual health conditions.
Medications and Insulin Therapy:
In Type 1 diabetes, insulin therapy is necessary as the body does not produce insulin. In Type 2 diabetes, oral medications, non-insulin injectables, or insulin may be prescribed, depending on the severity and progression of the disease.
It is crucial to take medications as prescribed and monitor their effectiveness. Regular communication with healthcare providers is essential to discuss any changes in medication or insulin dosage requirements.
Blood Sugar Monitoring:

Regular monitoring helps us understand how various factors, such as food, physical activity, stress, and medication, affect blood sugar levels. It provides valuable information for making adjustments to diet, exercise, and medication as needed.
Stress Management and Emotional Well-being:
Stress can significantly impact blood sugar levels in diabetics. Learning effective stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies can help maintain emotional well-being and prevent spikes in blood sugar. Support from family, friends, or diabetes support groups can provide a valuable network to share experiences and seek emotional support.
Education and Self-Care:
Diabetes education plays a crucial role in effective self-care. Understanding the disease, its management strategies and the importance of lifestyle modifications empowers individuals to take control of their health.

Diabetes self-management programs and resources provided by healthcare professionals can equip individuals with the knowledge and skills needed for successful diabetes management.
In conclusion:
Managing diabetes requires a holistic approach that includes medical care, healthy eating, regular physical activity, medications or insulin therapy, blood sugar monitoring, stress management, and education.
By adopting these strategies and working closely with your healthcare team, diabetics can lead fulfilling lives while effectively managing their condition. Remember, diabetes management is a lifelong journey, and each person’s plan may differ, so it’s crucial to personalize the management approach in collaboration with healthcare providers.
Read about how Concord Hospital Leveraged CPOE to Improve Diabetes Care Processes HERE!



 Exercise can help lower blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and maintain a healthy weight. Regular exercise can also help reduce the risk of heart disease, which is a common complication of diabetes. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. Consult with your healthcare provider before starting an exercise routine, especially if you have any diabetes-related complications.
Exercise can help lower blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and maintain a healthy weight. Regular exercise can also help reduce the risk of heart disease, which is a common complication of diabetes. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. Consult with your healthcare provider before starting an exercise routine, especially if you have any diabetes-related complications. Keeping track of your diabetes records is an important part of managing your condition. It can help you and your healthcare team make informed decisions about your treatment plan and identify any patterns or trends in your blood sugar levels.
Keeping track of your diabetes records is an important part of managing your condition. It can help you and your healthcare team make informed decisions about your treatment plan and identify any patterns or trends in your blood sugar levels.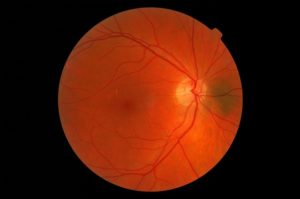 If your
If your While diabetic retinopathy can’t always be prevented, good management of your blood pressure and blood sugar levels, regular eye exams, and early detection and intervention can
While diabetic retinopathy can’t always be prevented, good management of your blood pressure and blood sugar levels, regular eye exams, and early detection and intervention can 
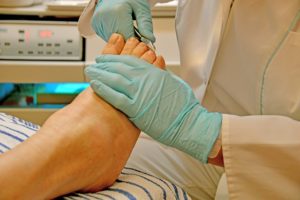 Trim your toenails after washing your feet, when they have been softened by water. Avoid cutting deep into the corners of your toes and use a nail file to smooth them. Check for any corners growing into the skin as this could potentially lead to ingrown toenails.
Trim your toenails after washing your feet, when they have been softened by water. Avoid cutting deep into the corners of your toes and use a nail file to smooth them. Check for any corners growing into the skin as this could potentially lead to ingrown toenails.